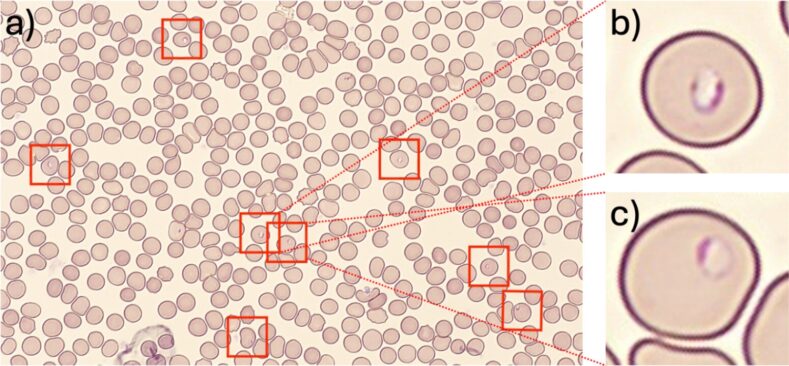
노을 주식회사(대표 임찬양, 이하 노을)는 자사의 말라리아 진단 솔루션 ‘miLab™ MAL’의 AI 진단 성능을 다룬 최신 연구 결과가 임상의학 분야 국제학술지인 Journal of Clinical Microbiology에 게재됐다고 밝혔다. 연구는 미국 최대 진단 랩 체인 랩콥(Labcorp)과 공동으로 진행했다.
이번 연구는 미국 내 랩콥의 레퍼런스 검사실에서 수집된 409개의 혈액 샘플을 기반으로 표준 현미경 검사와 노을의 miLab™ MAL 진단 결과를 비교해 진행됐다. 노스캐롤라이나, 사우스캐롤라이나, 버지니아, 컬럼비아특별구, 메릴랜드에 등 총 5개 지역 검사실에서 샘플이 수집됐다.
연구 결과 miLab™ MAL은 민감도(Sensitivity), 특이도(Specificity), 양성 예측도(PPV), 음성 예측도(NPV)에서 모두 100%를 기록하며, 표준 현미경 검사보다 우수한 진단 성능을 입증했다. 표준 현미경 검사의 경우, 민감도 81.8%, 특이도 100%, 양성 예측도 100%, 음성 예측도 99.5%를 보였다.
또한 miLab™ MAL은 표준 현미경 검사에서 놓친 위음성 사례를 모두 판별해 냈다. 연구에서 표준 현미경 전문가가 408개 샘플 중 399개는 음성, 9개는 양성으로 진단한 반면, miLab™ MAL은 동일 샘플에 대해 397개를 음성, 11개를 양성으로 진단했다. 현미경 검사에서 음성으로 판별된 2개 샘플을 재확인한 결과, 두 샘플 모두 극소량(<0.1%)의 기생충 감염(parasitemia)이 확인됐다.
miLab™ MAL은 20만 개의 적혈구를 분석해 기생충을 판별하며, 이는 표준 현미경에서 1천 개의 적혈구를 검사하는 것과 비교해 약 200배 많은 데이터를 기반으로 한다. 기존 연구에 따르면 표준 현미경 검사는 말라리아 감염 사례의 25% 이상을 놓칠 수 있어, miLab™ MAL은 특히 저농도 기생충 환경에서 높은 진단 정확도를 제공할 수 있는 혁신적인 도구로 주목 받고 있다.
팬데믹 이후 해외여행이 증가하면서 말라리아가 비유행 국가로 유입되는 사례가 꾸준히 증가하고 있다. 미국은 2018년 1,823건의 말라리아 유입 사례를 기록하며 지난 20년간 가장 높은 수치를 보였고, 2023년에는 플로리다, 메릴랜드, 텍사스 등 일부 주에서 비정상적인 감염 사례가 보고됐다. 이러한 상황에서 노을의 miLab™ MAL과 같은 AI 기반 말라리아 진단 솔루션의 필요성이 더욱 부각되고 있다.
- 관련 기사 더 보기
Noul's AI-based malaria diagnostic solution has been validated in international academic journals.

Noul Co., Ltd. (CEO Chan-Yang Lim, hereinafter referred to as Noul) announced that the latest research results on the AI diagnostic performance of its malaria diagnostic solution, "miLab™ MAL," were published in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology, an international academic journal in the field of clinical medicine. The research was conducted in collaboration with Labcorp, the largest diagnostic lab chain in the United States.
This study compared the results of standard microscopic examinations with those of Noul's miLab™ MAL diagnostics, based on 409 blood samples collected at LabCorp reference laboratories in the United States. Samples were collected from five regional laboratories: North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, the District of Columbia, and Maryland.
The study results showed that miLab™ MAL demonstrated superior diagnostic performance compared to standard microscopy, achieving 100% sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV). Standard microscopy demonstrated a sensitivity of 81.8%, a specificity of 100%, a positive predictive value of 100%, and a negative predictive value of 99.5%.
Additionally, miLab™ MAL identified all false-negative cases missed by standard microscopy. In the study, while the standard microscopist diagnosed 399 of 408 samples as negative and 9 as positive, miLab™ MAL diagnosed 397 of the same samples as negative and 11 as positive. Two samples that were negative by microscopy were re-examined and found to have very low levels of parasitic infection (<0.1%) in both samples.
miLab™ MAL analyzes 200,000 red blood cells to identify parasites, providing approximately 200 times more data than standard microscopy, which only examines 1,000 red blood cells. Previous studies have shown that standard microscopy can miss more than 25% of malaria cases, making miLab™ MAL a groundbreaking tool that can deliver high diagnostic accuracy, especially in low-parasite environments.
With the increase in international travel since the pandemic, cases of malaria being imported into non-endemic countries have steadily increased. The United States recorded 1,823 imported malaria cases in 2018, the highest number in the past 20 years, and unusual infections were reported in some states, including Florida, Maryland, and Texas, in 2023. This situation highlights the need for AI-based malaria diagnostic solutions, such as Noul's miLab™ MAL.
- See more related articles
Noul AIベースのマラリア診断ソリューション、国際学術誌を通じてパフォーマンスを証明

Noul株式会社(代表イム・チャンヤン、以下Noul)は、同社のマラリア診断ソリューション「miLab™ MAL」のAI診断性能を扱った最新の研究結果が臨床医学分野の国際学術誌であるJournal of Clinical Microbiologyに掲載されたと明らかにした。研究は、米国最大の診断ラボチェーンLabcorpと共同で行われた。
今回の研究は、米国内のラプコブのリファレンス検査室で収集された409個の血液サンプルに基づいて、標準顕微鏡検査とNoulのmiLab™ MAL診断結果を比較して行われた。ノースカロライナ、サウスカロライナ、バージニア、コロンビア特別区、メリーランドなど、計5つの地域検査室でサンプルが収集された。
研究の結果、miLab™MALは感度(Sensitivity)、特異度(Specificity)、陽性予測度(PPV)、陰性予測度(NPV)でいずれも100%を記録し、標準顕微鏡検査より優れた診断性能を実証した。標準顕微鏡検査の場合、感度81.8%、特異度100%、陽性予測も100%、陰性予測も99.5%を示した。
さらに、miLab™MALは、標準的な顕微鏡検査で見逃した偽陰性症例をすべて判別しました。研究では、標準顕微鏡の専門家が408サンプルのうち399は陰性、9は陽性と診断し、miLab™MALは同じサンプルに対して397を陰性、11を陽性と診断した。顕微鏡検査で陰性と判別された2つのサンプルを再確認した結果、両サンプルとも極少量(<0.1%)の寄生虫感染(parasitemia)が確認された。
miLab™MALは、20万個の赤血球を分析して寄生虫を判別し、これは標準顕微鏡で1000個の赤血球を検査するのと比較して約200倍のデータを基にしています。従来の研究によると、標準顕微鏡検査はマラリア感染症例の25%以上を見逃す可能性があり、miLab™MALは特に低濃度寄生虫環境で高い診断精度を提供できる革新的なツールとして注目されています。
ファンデミック以後海外旅行が増加し、マラリアが非流行国に流入する事例が着実に増加している。米国は2018年に1,823件のマラリア流入事例を記録し、過去20年間で最も高い数値を見せ、2023年にはフロリダ、メリーランド、テキサスなど一部の州で異常な感染事例が報告された。このような状況では、NoulのmiLab™MALなどのAIベースのマラリア診断ソリューションの必要性がさらに高まっています。
- 関連記事をもっと見る
Noul基于人工智能的疟疾诊断解决方案已在国际学术期刊上得到验证。

Noul株式会社(代表理事长林灿阳,以下简称“Noul”)宣布,其疟疾诊断解决方案“miLab™ MAL”的AI诊断性能最新研究成果已发表在临床医学领域国际学术期刊《临床微生物学杂志》上。该研究由Noul与美国最大的诊断实验室连锁机构Labcorp合作开展。
本研究基于美国LabCorp参考实验室采集的409份血液样本,将标准显微镜检查结果与Noul的miLab™ MAL诊断结果进行了比较。样本来自五个地区实验室:北卡罗来纳州、南卡罗来纳州、弗吉尼亚州、哥伦比亚特区和马里兰州。
研究结果表明,miLab™ MAL 的诊断性能优于标准显微镜,灵敏度、特异性、阳性预测值 (PPV) 和阴性预测值 (NPV) 均达到 100%。标准显微镜的灵敏度为 81.8%,特异性为 100%,阳性预测值为 100%,阴性预测值为 99.5%。
此外,miLab™ MAL 还能识别标准显微镜检查遗漏的所有假阴性病例。在研究中,标准显微镜检查员将 408 个样本中的 399 个诊断为阴性,9 个诊断为阳性,而 miLab™ MAL 则将相同的样本中 397 个诊断为阴性,11 个诊断为阳性。对两个显微镜检查结果为阴性的样本进行了重新检查,结果发现这两个样本的寄生虫感染水平都非常低(<0.1%)。
miLab™ MAL 可分析 20 万个红细胞来识别寄生虫,提供的数据量比仅检测 1000 个红细胞的标准显微镜检查高出约 200 倍。先前的研究表明,标准显微镜检查可能会漏诊超过 25% 的疟疾病例,这使得 miLab™ MAL 成为一种突破性的工具,能够在低寄生虫环境中提供高诊断准确性。
自疫情爆发以来,随着国际旅行的增加,输入非疟疾疫区的疟疾病例也稳步增加。美国在2018年记录了1,823例输入性疟疾病例,为过去20年来的最高值。2023年,佛罗里达州、马里兰州和德克萨斯州等一些州报告了异常感染病例。这种情况凸显了对基于人工智能的疟疾诊断解决方案的需求,例如Noul的miLab™ MAL。
- 查看更多相关文章
La solution de diagnostic du paludisme basée sur l’IA de Noul a été validée dans des revues universitaires internationales.

Noul Co., Ltd. (PDG Chan-Yang Lim, ci-après dénommée Noul) a annoncé la publication des derniers résultats de recherche sur les performances diagnostiques de l'IA de sa solution de diagnostic du paludisme, « miLab™ MAL », dans le Journal of Clinical Microbiology, une revue académique internationale spécialisée dans la médecine clinique. Cette recherche a été menée en collaboration avec Labcorp, la plus grande chaîne de laboratoires de diagnostic des États-Unis.
Cette étude a comparé les résultats d'examens microscopiques standard à ceux du diagnostic miLab™ MAL de Noul, à partir de 409 échantillons sanguins prélevés dans les laboratoires de référence LabCorp aux États-Unis. Les échantillons ont été prélevés dans cinq laboratoires régionaux : Caroline du Nord, Caroline du Sud, Virginie, District de Columbia et Maryland.
Les résultats de l'étude ont montré que miLab™ MAL offrait des performances diagnostiques supérieures à celles de la microscopie standard, avec une sensibilité, une spécificité, une valeur prédictive positive (VPP) et une valeur prédictive négative (VPN) de 100 %. La microscopie standard a démontré une sensibilité de 81,8 %, une spécificité de 100 %, une valeur prédictive positive de 100 % et une valeur prédictive négative de 99,5 %.
De plus, miLab™ MAL a identifié tous les cas faussement négatifs manqués par la microscopie standard. Dans l'étude, alors que le microscopiste standard a diagnostiqué 399 échantillons sur 408 comme négatifs et 9 comme positifs, miLab™ MAL a diagnostiqué 397 de ces mêmes échantillons comme négatifs et 11 comme positifs. Deux échantillons négatifs à la microscopie ont été réexaminés et présentaient de très faibles taux d'infection parasitaire (< 0,1 %).
miLab™ MAL analyse 200 000 globules rouges pour identifier les parasites, fournissant environ 200 fois plus de données que la microscopie standard, qui n'examine que 1 000 globules rouges. Des études antérieures ont montré que la microscopie standard peut passer à côté de plus de 25 % des cas de paludisme, faisant de miLab™ MAL un outil révolutionnaire offrant une grande précision diagnostique, notamment dans les environnements à faible parasitémie.
Avec l'augmentation des voyages internationaux depuis la pandémie, les cas de paludisme importés dans les pays non endémiques n'ont cessé d'augmenter. Les États-Unis ont enregistré 1 823 cas de paludisme importés en 2018, soit le nombre le plus élevé des 20 dernières années, et des infections inhabituelles ont été signalées dans certains États, dont la Floride, le Maryland et le Texas, en 2023. Cette situation souligne la nécessité de solutions de diagnostic du paludisme basées sur l'IA, telles que miLab™ MAL de Noul.
- Voir plus d'articles connexes
You must be logged in to post a comment.